Operate First Aid Equipment According to Manufacturer's Instructions
First, it's important to realize that a CPR mask, officially known as a barrier device, is for keeping you -- the rescuer -- safe. It doesn't make rescue breaths more effective than straight mouth-to-mouth.
For an intimate partner or immediate family member, a barrier device is probably not necessary unless the victim is known to have an infectious disease. It's probably not even necessary for performing mouth-to-mouth on a stranger in the grocery store, but we'll get to that in a moment.
Different Types of Barrier Devices
A barrier device is one type of personal protective equipment designed to protect rescuers from exposure to infection when in close contact with victims. HIV and the hepatitis family of viruses are carried in blood and some other body fluids. Since there is no way to know if the victim of a cardiac arrest is carrying these or any other communicable diseases, it's wise to use a barrier device to keep body fluids out of the rescuer's mouth during rescue breathing.
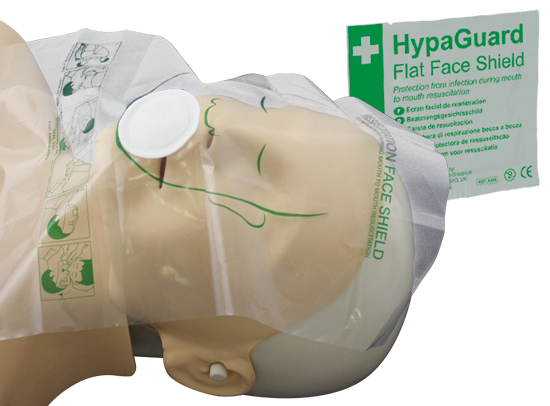
There are 2 types of barrier devices used by lay rescuers:
- A flat plastic barrier that lies across the victim's mouth and nose. It conforms to the face and allows the rescuer to blow through a hole in the middle. The hole has either a one-way valve or a filter to protect the rescuer, depending on the brand. These flat barriers are popular with lay rescuers (and off-duty professionals) because they are so portable. Most of the time, they can fold up tight and fit on a keychain.
- A mask shaped like a pear that fits over the mouth and nose. With proper technique, it seals around the mouth and nose. The rescuer blows through a one-way valve at the top to provide rescue breaths.
To an untrained eye, these can look like complicated devices. For most lay rescuers, a flat barrier is probably the best device on the market because of its ease of use and portability. The technique required for making a seal with mask devices is difficult to learn and very hard to perfect.
Flat face shield
This is a flat piece of plastic which is put across the casualties' mouth and then the normal resuscitation breaths can be given using the correct technique. The face shield usually has a one way valve , which is placed between the casualties' lips this is to stop any fluid such as vomit being brought up, going into the helper mouth.
Pocket mask
A pocket mask, or pocket face mask or CPR mask, is a device used to safely deliver rescue breaths during a cardiac arrest or respiratory arrest.
The pocket mask is a small device that can be carried on one's person. Air is administered to the patient when the emergency responder exhales through a one-way filter valve. Modern pocket masks have either a built in one-way valve or an attachable, disposable filter to protect the emergency responder from the patient's potentially infectious bodily substances, such as vomit or blood.
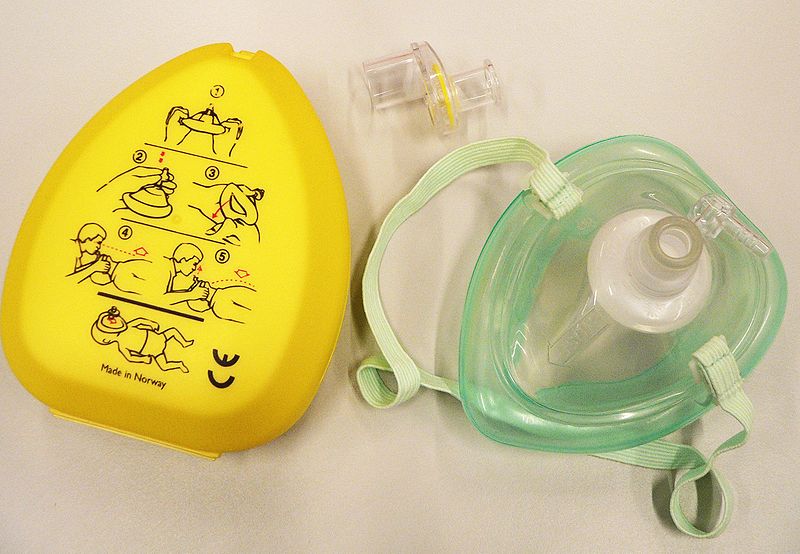
Many masks also have a built-in oxygen intake tube, allowing for administration of 50-60% oxygen. Without being hooked up to an external line, exhaled air from the provider can still provide sufficient oxygen to live, up to 16%. Earth's atmosphere consists of approximately 21% oxygen
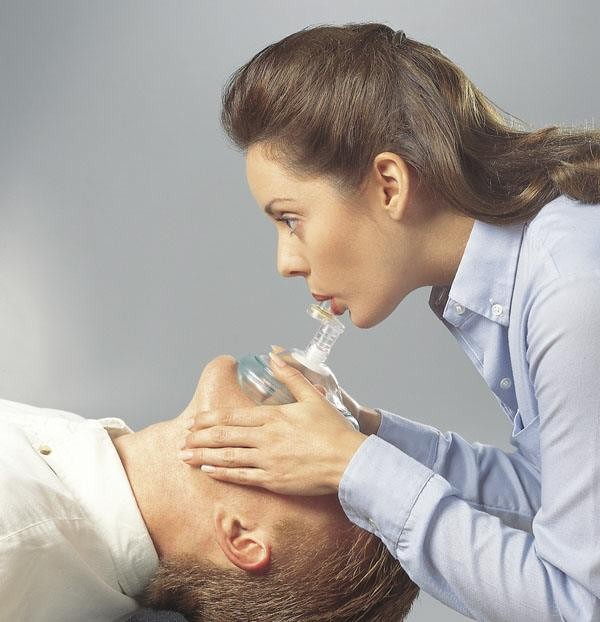 While a pocket mask is not as efficient as a bag valve mask, it does have its advantages when only one rescuer is available. As suggested by its name, the pocket mask benefits from a somewhat easier portability when compared to the bag valve mask. Also, in contrast to the bag valve mask, which requires two hands to operate (one to form a seal and the other to squeeze the bag), the pocket mask allows for both of the rescuer's hands to be on the patients head. This hand placement provides a superior seal on the patient's face, and allows the responder to perform a jaw thrust on patients suspected of a spinal injury.
While a pocket mask is not as efficient as a bag valve mask, it does have its advantages when only one rescuer is available. As suggested by its name, the pocket mask benefits from a somewhat easier portability when compared to the bag valve mask. Also, in contrast to the bag valve mask, which requires two hands to operate (one to form a seal and the other to squeeze the bag), the pocket mask allows for both of the rescuer's hands to be on the patients head. This hand placement provides a superior seal on the patient's face, and allows the responder to perform a jaw thrust on patients suspected of a spinal injury.
Automated external
The heart is a muscular pump, approximately the same size as its owner's fist and is located behind and slightly to the left of the breastbone. Its function is to pump oxygen-rich blood from the lungs to various parts of the body and to pump the de-oxygenated blood from the tissues back to the lungs to take on more oxygen.
Pumping blood through the lungs removes carbon dioxide and re-supplies the blood with oxygen. The newly oxygenated blood is then pumped around the body to provide oxygen and nutrients and remove waste products.
The heart's mechanical action;
The heart has four chambers with one-way flaps called valves between the upper and lower chambers. The atria are the upper chambers and they receive blood that is being returned to the heart.
When the atria pump (contract), they push the blood through valves into the relaxed ventricles (lower chambers), when the ventricles contract, the right ventricle pumps blood into the lungs. It is the pressure of the blood reflected on the walls of the arteries which is felt as a pulse.
A normal healthy adult heart beats rhythmically at a rate of about 60 to 100 beats a minute when at rest, during strenuous exercise, the heart can increase the amount of blood it pumps up to four times the amount it pumps at rest within only a matter of seconds.