Classifications of shock severity
| Observation | Healthy | Shocked |
| Skin condition | Pink, warm, dry | Pale, cold, wet |
| Conscious state | Alert and aware of | time and place |
|
Pulse - Adult Child Infant |
Per minute 60 - 100 90 - 130 120 - 160 |
Rapid - above upper limits |
|
Respiration Adult Child Infant |
Per minute 12 - 20 16 - 25 20 - 30 |
Rapid - above upper limits |
Burns and scalds
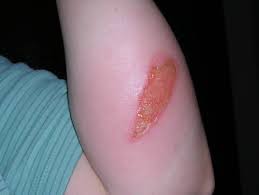
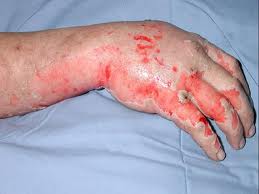
Burns are injuries that damage and kill skin cells and are most commonly caused by exposure to flames, hot objects, hot liquids, chemicals, radiation or a combination of these. Scalds are caused by contact with wet heat such as boiling fluids or steam. Electrical burns are less common, but have the potential to be more serious as the depth of the burn is usually greater than is apparent and heart irregularities may occur.
 As with most potentially serious injuries, prevention is better than cure. All homes should be fitted with smoke detectors. Keep hot objects, such as kettles, safely out of reach of children and make sure to turn off heaters and stoves when not in use.
As with most potentially serious injuries, prevention is better than cure. All homes should be fitted with smoke detectors. Keep hot objects, such as kettles, safely out of reach of children and make sure to turn off heaters and stoves when not in use.
Also keep all electrical wires away from water, place socket caps over all unused electrical sockets and have your leads tested and tagged regularly. Keep household chemicals out of reach of children, ensure these are well marked and their caps are screwed on tight.
Burns are most commonly caused by exposure to flames, hot objects, hot liquids, chemicals or radiation.
Scalds are caused by contact with wet heat such as boiling fluids or steam. A doctor should see infants or children who receive any burns.
It is important that any casualty who has inhaled smoke, fumes or superheated air or has been burnt on the face, seeks medical aid as soon as possible after the incident.
Electrical burns have the potential to be more serious as the depth of the burn is usually greater than is apparent and cardiac (heart) irregularities may occur.
Burns are classified as either:
Superficial
- Reddening (like sunburn)
- Damage to outer layer of skin only
Partial thickness
- Blistering
- Damage to outer layer of skin
Full thickness
- White or blackened areas
- Damage to all layers of skin, plus underlying structures and tissues
Signs and symptoms
- Red, blistered, white or blackened skin
- Signs of shock
- Pain in superficial and partial thickness burns
- Breathing difficulties
- Hoarse voice and/or snoring sound when breathing
Care and treatment
- Ensure safety
- Call Triple Zero(000) for an ambulance
- Put on disposable gloves if available
- Cool only with clean water if possible and resist using other substances - up to 20 minutes for thermal or radiation burns - for at least 20 minutes for chemical burns - for at least 30 minutes for bitumen burns - if medical assistance is delayed and the limb is completely encircled, split the bitumen lengthwise as it cools - keep phosphorous burns wet at all times
- Remove phosphorus particles using forceps only
- Cover with a clean, non-stick sterile dressing (or plastic wrap etc.)
- Remove tight clothing and objects, e.g. rings, jewellery
- Treat for shock if the burn is severe
- Ensure contaminated or smoldering clothing is removed unless it is sticking to the skin
- Flush chemicals from the skin, pay special attention to eyes
- Do not break blisters.
- Do not attempt to remove bitumen from the skin or eyes.
- Avoid the use of lotions and creams.
- Ensure cooling is not excessive resulting in shivering
Burns to the face may have an effect on the casualty's breathing and these effects may take some time to appear. Seek medical aid if the:
- Burn is larger than the casualty's palm
- Casualty has inhaled smoke, fumes or superheated air
- Casualty is an infant or child
- Burns involve the hands, face or genitals
- Burn was caused by: - lasers - industrial microwave equipment - infra-red or ultra-violet rays - nuclear radiation
Hydrogel dressings or gel are a suitable alternative when water is not available.