Welder's flash
Flash burn and welder's flash is the result of staring or inadvertently looking at the intense light caused during metal welding, while not wearing the correct eye protection. Care must be taken to supervise children if welding is being conducted near them and they should be removed from the location. The damage caused to the eye's cornea by exposure to this intense light can be painful and in some cases, permanent.
Care and treatment:
- Apply cool compresses and cover the eyes with pads
- Urgent medical attention if pain or spots persist
Tooth injuries
The structure of the tooth includes dentin, pulp and other tissues, blood vessels and nerves embedded in the bony jaw. Above the gum line, the tooth is protected by the hard enamel covering. When a tooth is knocked out, appropriate emergency medical and dental care is necessary.
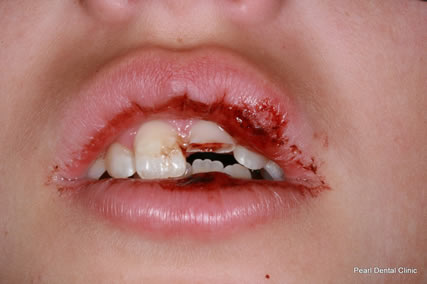 If a child is 7 years of age or older it is likely to be a second or permanent tooth. A second or permanent tooth can often be saved if prompt action is taken and the tooth is handled carefully. The delicate tissue covering the root must be protected to ensure successful re-implantation.
If a child is 7 years of age or older it is likely to be a second or permanent tooth. A second or permanent tooth can often be saved if prompt action is taken and the tooth is handled carefully. The delicate tissue covering the root must be protected to ensure successful re-implantation.
If a child is 6 years of age or younger it is likely to be a baby or primary tooth. Baby teeth may become injured after a fall and turn grey in colour. Treatment is not always necessary, but it is best to have the dentist examine the child as soon as possible.
Care and treatment:
- When a baby or toddler injures gums or teeth:
- If there is bleeding, put cold water on a piece of gauze and apply pressure to the site
- Offer the casualty an icy pole or ice cube to suck, to reduce swelling
- Call your dentist. They will probably want to see the child to assess the need for realignment or removal of a very loose tooth
- If a permanent tooth is knocked out:
- Hold the tooth by the crown (chewing edge), not the root
- Rinse the tooth immediately with saline solution or milk, avoid scrubbing material off it. If this is not possible, wrap in plastic cling wrap
- If the casualty will co-operate, replace the tooth gently in its socket
- Have the casualty bite down gently on a gauze pad to keep the tooth in place
- If the tooth cannot be re-inserted, put it in milk which is a good preservative because its chemical make-up is compatible with teeth
- If milk is not available, the tooth can be placed in the casualty's mouth between the teeth and cheek, if old enough not to swallow the tooth. If this is not possible, wrap in plastic cling wrap
- Give the casualty a gauze pad or handkerchief to gently bite down on, which will help control bleeding and ease the pain
- See a dentist right away, within 20 minutes if possible
Do not replace the tooth or place anything in the mouth of a drowsy or unconscious casualty.
If the tooth can't be re-implanted, control bleeding by placing a gauze pad in the tooth socket and then get the casualty to bite gently down on the pad. Avoid rinsing out the mouth because this can interfere with blood clotting. If the gums are bleeding, put cold water on a piece of gauze and push it between the lips and gums. Have the casualty hold pressure on the bleeding site.
Fainting
Fainting occurs when the blood supply to the brain is momentarily inadequate, causing a brief loss of consciousness. Fainting is usually caused by a relatively minor event such as the sight of blood or just prior to receiving an injection.
Fainting can have no medical significance or the cause can be a serious disorder. Therefore, treat loss of consciousness as a medical emergency until the signs and symptoms are relieved and the cause is known.
There are many causes of fainting, including:
- Standing for long periods
- The sight of needles
- The sight of blood
- Pain
- Emotional events
- Heat
Sign and symptoms:
- Dizziness or feeling light headed
- Nausea
- Pale, cool and clammy skin
- Anxious
- Collapse
- Loss of consciousness
- Rapid recovery after being laid flat
Care and treatment:
Simple faint
- If unconscious - recovery position
- Raise the legs if possible
- If conscious - lay the casualty flat and raise the legs if possible
- If not fully recovered in a few minutes, call Triple Zero (000) for an ambulance
- If the casualty was injured in the fall, treat any injuries appropriately
- Heat syncope
- Recovery position
- Cool casualty by fanning
- Loosen and remove excessive clothing