Chickenpox (varicella)
Chickenpox is very contagious. It is a viral disease, usually mild in children. It can be
more serious in adults. Complications from the disease are rare and are usually restricted to infections of the chickenpox blisters.
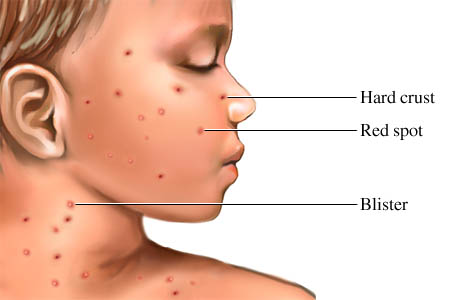 Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms
- Mild fever (38-40ºC)
- Illness for 1 or 2 days
- Skin eruptions or blisters
- that appear anywhere on
- the body, including:
- mouth
- nose
- penis
- vagina
- head
Limbs are least affected. The blisters form scabs after 24 hours and new blisters appear every 2 - 3 days.
Care and treatment
- The application of cool compresses reduces the 'itchiness' of the blisters and discourages scratching by the child
- Contact your GP or local child health centre for advice
- A vaccine has been developed to prevent chickenpox
Measles
The common form of measles is a serious viral illness that infects the skin and, more importantly, the respiratory tract.
Measles is highly contagious and can be fatal to those communities that have no historical immunity, such as the indigenous population.
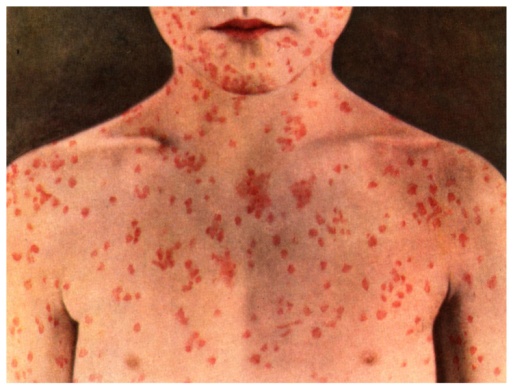 The incubation period is 7-12 days after exposure and possible complications associated with the disease are pneumonia, meningitis or encephalitis. Measles is becoming more common in the community after a period of low incidence.
The incubation period is 7-12 days after exposure and possible complications associated with the disease are pneumonia, meningitis or encephalitis. Measles is becoming more common in the community after a period of low incidence.
Signs and symptoms
- Fever (39ºC+)
- Sneezing
- Runny nose
- Harsh, hacking, dry cough
- Red eyes sensitive to light
- White spots in the mouth and throat
- Red rash spreading from the ears and forehead to the rest of the body
Care and treatment
- Contact your GP for treatment and advice
- Encourage the child not to watch TV or read as this exacerbates the child's sensitivity to light and makes the eyes irritable
- Keep constant observation of the child's temperature
A vaccine against measles is available and recommended for children between 12 and 15 months. It is combined with the mumps and rubella vaccines.
German measles (rubella)
Rubella is a viral illness, usually mild in onset. The danger with this illness is in the spread to pregnant women. A woman who contracts rubella in the first 3 or 4 months of pregnancy is at risk of giving rise to severe defects in the unborn child. Rubella is preventable by immunisation and all non-pregnant females of child-bearing age should be immunised.
Signs and symptoms
- Slight fever
- Muscle aches
- Stiff neck, fatigue
- Slight red rash on the child's head and body after 2-3 days
- Swollen neck lymph glands
Care and treatment
- Contact your GP for advice
- Ensure your child does not have known contact with pregnant women
The child usually recovers within a week.
Tonsillitis (pharyngitis)
Tonsillitis is the inflammation of the lymph tissue at the back of the throat. Tonsils are at their largest and most susceptible to infection, between the ages of 4 years and puberty.
There are many possible, highly contagious, bacterial and viral causes of tonsillitis.
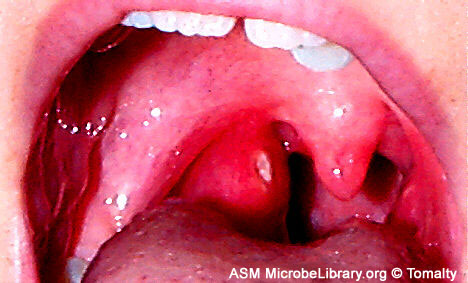 Signs and symptoms
Signs and symptoms
- Pain in the throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chills
- Fever (40ºC or greater)
- Swollen glands above the jaw
- Headache, earache
- Cough (rarely)
Care and treatment
Contact your GP or child health centre for advice. Some infections indicate antibiotics may be required. Repeated bouts of tonsillitis may necessitate surgery to remove the tonsils.